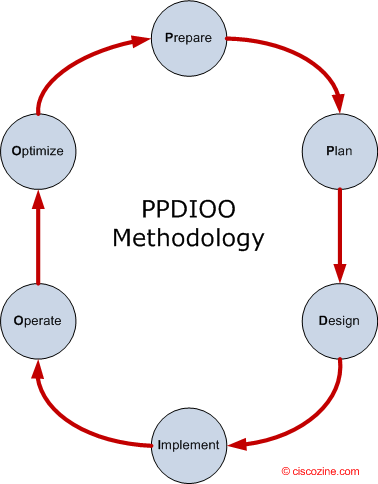
One of the first topic presented in the “Designing for Cisco Internetwork Solutions (DESGN)” book is about the network design methodology. This methodology is composed by six phases closely related: prepare, plan, design, implement, operate, optimize.
As show in this figure, the PPDIOO lifecycle phases are separate, yet closely related.
Why use the PPDIOO model?
- Lowering the total cost of network ownership: Companies try to lower the total cost of network ownership while they add new technologies to an existing network, procure equipment, train staff, manage network performance, and maintain the network.
- Improving business agility: Business agility can be described as an organization’s ability to respond rapidly to changing business or market conditions and adapt to the changing demands of its customers and the business environment. “In the long term,” industry analyst Gartner writes, “perhaps the most important role for business leaders is to identify the agenda for agility and to prepare the organization to face threats.”
- Speeding access to applications and services: Speeding access to applications and services helps enable business agility. For example, an IP Communications system could be outfitted with a customer relationship application that enables incoming calls to automatically trigger the display of customer account information and contact history, providing staff with the information they need to respond quickly and effectively.
- Increasing availability: Downtime can adversely affect revenue and can reduce profitability through costs associated with the network staff having to troubleshoot and function in a reactive mode. High availability depends on carefully planned redundancy, sound security, and scalability and also requires diligence throughout the network lifecycle. Availability targets are influenced by business goals. Targets are established early in the network lifecycle and achieved throughout it: a smooth, well-planned deployment helps minimize risk of downtime, and sound planning for day-to-day operations helps speed problem resolution.
PPDIOO phases:
- Prepare phase: Business agility starts with preparation: anticipating the broad vision, requirements, and technologies needed to build and sustain a competitive advantage. In the prepare phase, a company determines a business case and financial rationale to support the adoption of new technology. By carefully anticipating future needs and developing both a technology strategy and a high-level architecture to meet those needs, a business is better equipped to contain costs during deployment and operations.
- Plan phase: Successful technology deployment depends on an accurate assessment of a company’s current network, security state, and overall readiness to support the proposed solution. In the plan phase, a company ascertains whether it has adequate resources to manage a technology deployment project to completion. To evaluate and improve network security, a company tests its network for vulnerability to intruders and outside networks. The company then develops a detailed project plan to identify resources, potential difficulties, individual responsibilities, and critical tasks necessary to deliver the final project on time and on budget.
- Design phase: Developing a detailed design is essential to reducing risk, delays, and the total cost of network deployments. A design aligned with business goals and technical requirements can improve network performance while supporting high availability, reliability, security, and scalability. Day-to-day operations and network management processes need to be anticipated, and, when necessary, custom applications are created to integrate new systems into existing infrastructure. The design phase can also guide and accelerate successful implementation with a plan to stage, configure, test, and validate network operations.
- Implement phase: A network is essential to any successful organization, and it must deliver vital services without disruption. In the implement phase, a company works to integrate devices and new capabilities in accordance with the design—without compromising network availability or performance. After identifying and resolving potential problems, the company attempts to speed return on investment with an efficient migration and successful implementation—including installing, configuring, integrating, testing, and commissioning all systems. After network operation is validated, an organization can begin expanding and improving IT staff skills to further increase productivity and reduce system downtime.
- Operate phase: Network operations represent a significant portion of IT budgets, so it’s important to be able to reduce operating expenses while continually enhancing performance. Throughout the operate phase, a company proactively monitors the health and vital signs of the network to improve service quality; reduce disruptions; mitigate outages; and maintain high availability, reliability, and security. By providing an efficient framework and operational tools to respond to problems, a company can avoid costly downtime and business interruption. Expert operations also allow an organization to accommodate upgrades, moves, additions, and changes while effectively reducing operating costs.
- Optimize phase: A good business never stops looking for a competitive advantage. That is why continuous improvement is a mainstay of the network lifecycle. In the optimize phase, a company is continually looking for ways to achieve operational excellence through improved performance, expanded services, and periodic reassessments of network value. Have business goals or technical requirements changed? Is a new capability or enhanced performance recommended? As an organization looks to optimize its network and prepares to adapt to changing needs, the lifecycle begins anew—continually evolving the network and improving results.
References:

Congratulations. This methodology is very good. Gratz Cisco
I would like to personally congrat Cisco too, good job buddies !
long winded and boring