The spanning-tree protocol is used to cut loops that redundant links create in bridge networks. These packets are not attested by the system, so an attacker could spoof the BPDU and compromise the network stability!
See below to understand BPDU attack:
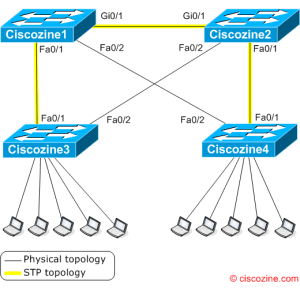
In this example the Ciscozine1 switch is elected Root Bridge due to the lower MAC-address (suppose that all the switches have the same priority).
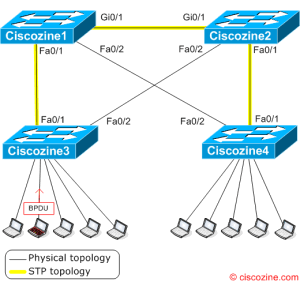
What happen if an attacker (in this instance a laptop) spoof a BPDU with a lower priority?
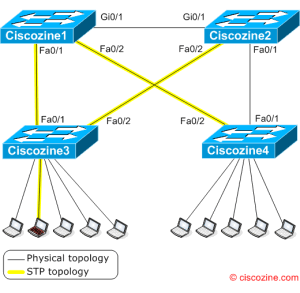
The attacker (red laptop) will be the new root bridge and the spanning-tree topology change. See the figure:
With this new topology, Ciscozine3 and Ciscozine4 use only Ciscozine1 to switch packets, while Ciscozine2 is not used by the access switches (Ciscozine3 and Ciscozine4)!
Moreover the election of the attacker as root causes the Gigabit Ethernet link that connects the two core switches (Ciscozine1 and Ciscozine2) to block, causing suboptimal network.
Note: The administrator can set the root bridge priority to zero in an effort to secure the root bridge position, but there is no guarantee against a bridge with a priority of 0 and a lower MAC address.
Note: The temporary introduction and subsequent removal of STP devices with low (0) bridge priority cause a permanent STP recalculation.
How can I protect myself against BPDU spoof attack?
Cisco has implemented three different solutions: BPDU Guard, BPDU Filtering and Root Guard.
BPDU Guard
The STP PortFast BPDU guard enhancement allows network designers to enforce the STP domain borders and keep the active topology predictable. The devices behind the ports that have STP PortFast enabled are not able to influence the STP topology. At the reception of BPDUs, the BPDU guard operation disables the port that has PortFast configured. The BPDU guard transitions the port into errdisable state, and a message appears on the console.
You can enable or disable STP PortFast BPDU guard on a global basis, which affects all ports that have PortFast configured. By default, STP BPDU guard is disabled.
To enable BPDU guard globally on the switch, use this command:
Ciscozine3(config)#spanning-tree portfast bpduguard default
To enable PortFast BPDU guard on a specific switch port, use this command:
Ciscozine3(config)#spanning-tree bpduguard enable
Use the following command to verify the BPDU configuration:
Ciscozine3#show spanning-tree summary totals
The STP PortFast BPDU guard was introduced in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1.
Note: STP PortFast BPDU guard is not available for the Catalyst 8500 series, 2948G-L3, or 4908G-L3 switches.
Note: You must manually reenable the port that is put into errdisable state or configure errdisable-timeout.
BPDU Filterning
When configured globally, PortFast BPDU filtering applies to all operational PortFast ports. Ports in an operational PortFast state are supposed to be connected to hosts, that typically drop BPDUs. If an operational PortFast port receives a BPDU, it immediately loses its operational PortFast status. In that case, PortFast BPDU filtering is disabled on this port and STP resumes sending BPDUs on this port.
PortFast BPDU filtering can also be configured on a per-port basis. When PortFast BPDU filtering is explicitly configured on a port, it does not send any BPDUs and drops all BPDUs it receives.
To enable PortFast BPDU filtering globally on the switch, use this command:
Ciscozine3(config)#spanning-tree portfast bpdufilter default
To enable PortFast BPDU filtering on a specific switch port, use this command:
Ciscozine3(config-if)#spanning-tree bpdufilter enable
To verify the configuration on the switch, use this command:
Ciscozine3#show spanning-tree summary
The STP PortFast BPDU filtering was introduced in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(13)E.
Remember: Explicit configuration of PortFast BPDU filtering on a port not connected to a host station can result in bridging loops. The port ignores any incoming BPDUs and changes to the forwarding state. This does not occur when PortFast BPDU filtering is enabled globally.
BPDU Root guard
The root guard ensures that the port on which root guard is enabled is the designated port. Normally, root bridge ports are all designated ports, unless two or more ports of the root bridge are connected together. If the bridge receives superior STP Bridge Protocol Data Units (BPDUs) on a root guard-enabled port, root guard moves this port to a root-inconsistent STP state. This root-inconsistent state is effectively equal to a listening state. No traffic is forwarded across this port. In this way, the root guard enforces the position of the root bridge.
To enable Root Guard on a specific switch port, use this command:
Ciscozine3(config-if)#spanning-tree rootguard
Root guard is available in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(5)XU and later. The Catalyst 2950 series switches support the root guard feature in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.0(5.2)WC(1) and later. The Catalyst 3550 series switches support the root guard feature in Cisco IOS Software Release 12.1(4)EA1 and later.
Note: You must manually reenable the port that is put into errdisable state or configure errdisable-timeout.
Conclusion: In my opinion, BPDU Guard control BPDU spoof attack much better than BPDU Filtering. As a matter of fact, BPDU Guard block immediately the port at the reception of BPDUs, whereas BPDU Filtering only disable portfast feature.
The root guard feature partially restricts this type of attack; in fact an attacker will not be the root bridge, but it could take part of the spanning-tree instance.
For these reasons, a good solution to block BPDU spoof attack is to enable BPDU Guard control at all fastethernet ports used to connect laptop/PC/Server, while enable root guard feature on the ports used to connect switches.
References:

Cool article, I enjoy your blog very much. Just one question about this article… with enabling BPDU Guard per port, I assume you should be in interface config rather than global config?
Thanks
Terryn.
Yes, sure!
The BPDU Guard feature defines a “per-port” feature, so it is defined in the interface config.
Great blog.
Can you tell me what happens when a port configured with portfast but no bpdu guard receives a bpdu?
PortFast should be used only when connecting a single end station to a switch port. If you enable PortFast on a port connected to another networking device, such as a switch, you can create network loops.
One more thing i believe that root primary is stronger then priority zero, priority ± vlan id so bridge id is never 0. This is why you should shutdown all ports and on active one use portsecurity with only one MAC address